주메뉴
- About IBS 연구원소개
-
Research Centers
연구단소개
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research(Neuro Technology Group)
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research(Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience Group)
- Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis
- Center for Genome Engineering
- Center for Nanomedicine
- Center for Biomolecular and Cellular Structure
- Center for 2D Quantum Heterostructures
- Center for Quantum Conversion Research
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center 뉴스 센터
- Career 인재초빙
- Living in Korea IBS School-UST
- IBS School 윤리경영


주메뉴
- About IBS
-
Research Centers
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research(Neuro Technology Group)
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research(Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience Group)
- Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis
- Center for Genome Engineering
- Center for Nanomedicine
- Center for Biomolecular and Cellular Structure
- Center for 2D Quantum Heterostructures
- Center for Quantum Conversion Research
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center
- Career
- Living in Korea
- IBS School
News Center
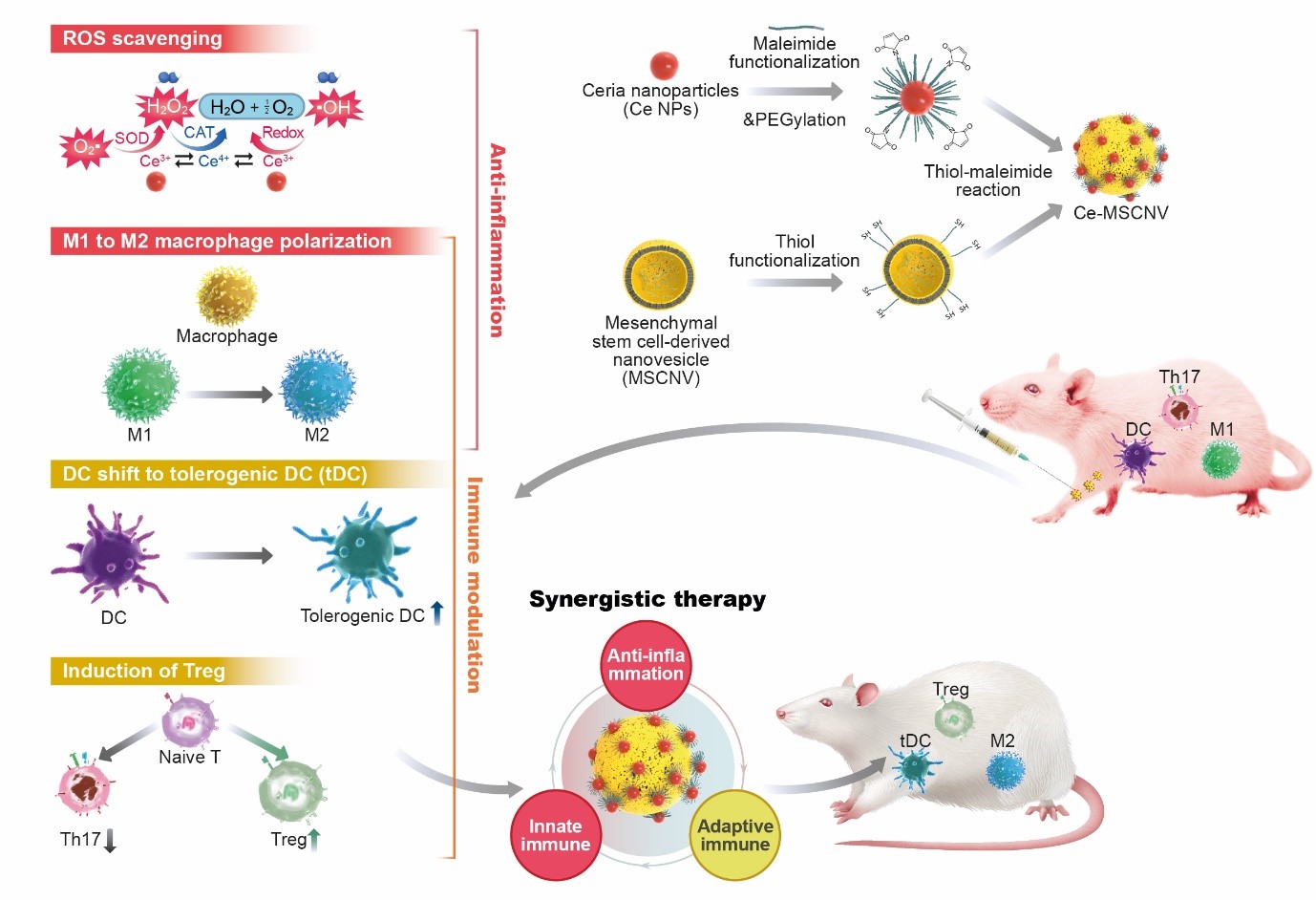
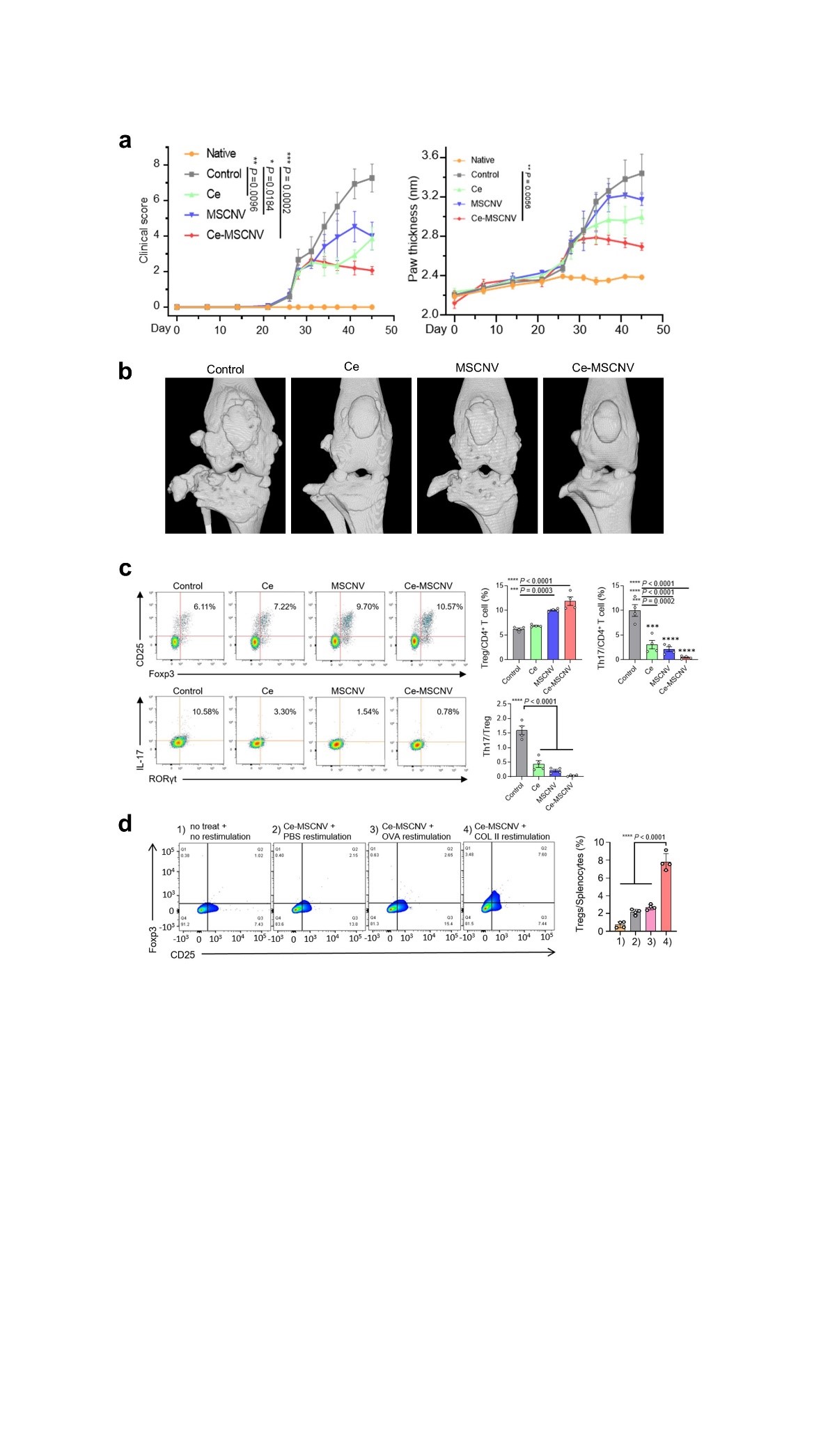
New nanoparticles found to be effective for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis- Ceria nanoparticle-immobilized mesenchymal stem cell nanovesicle hybrid system offers both immediate pain relief and long-term immune tolerance - A team of scientists led by KOO Sagang from the Seoul National University and Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institue for Basic Science Center (IBS), in collaboration with researchers from Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and the Seoul National University, developed a new solution for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is a chronic disease that, unfortunately, has no cure. The disease triggers a mix of troublesome symptoms like inflamed joints, harmful cytokines, and immune system imbalances, which work together to create a relentless cycle of worsening symptoms. While targeting some of these factors can provide short-term relief, others remain unresolved, leading to a frustrating cycle of remission and flare-ups. One of the major hurdles in RA treatment is the inability to restore the immune system to its healthy state. This leaves the body unable to control the continuous production of harmful substances like reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines, leading to persistent inflammation and discomfort. In essence, the ideal treatment for RA should not only provide immediate relief from inflammation and symptoms but also address the root cause by restoring the immune system to its normal, balanced state. New nanoparticle-based system as a solution The new platform involves immobilizing ceria nanoparticles (Ce NPs) onto mesenchymal stem cell-derived nanovesicles (MSCNVs). Both of these components can hinder different pathogenic factors, allowing them to work both individually and cooperatively to achieve a comprehensive treatment. Ce NPs - can scavenge the overproduced ROS in RA-inflicted knee joints. They also induce polarization of M1 macrophages into M2, achieving immediate relief of inflammation and symptoms. MSCNVs - deliver immunomodulatory cytokines, which turn dendritic cells (DC) into tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs). This consequently generates regulatory T cells for long-term immune tolerance. In short, this approach aims to bridge both innate and adaptive immunity to achieve both short-term pain relief, as well as convert the tissue environment into an immune-tolerant state to prevent the recurrence of symptoms. Researchers confirmed the efficacy of this approach using a collagen-induced arthritis mouse model. The Ce-MSCNV system was able to comprehensively treat and prevent RA by simultaneously relieving the immediate and restoring T cell immunity. Supporting data suggest that improvement in conditions can be achieved after only a single-dose treatment. The mice treated with the Ce-MSCNV combination fared far better compared to the ones only treated using the Ce NP or MSCNV group. This clearly demonstrates the synergy between anti-inflammation and immunomodulation and underlines the importance of the combined therapy for effective RA treatment. In addition, Ce-MSCNV administration prior to booster injection markedly reduced the incidence and severity of symptoms, supporting the prophylactic potential of these nanoparticles. First author KOO Sagang stated, “One of the hardest decisions in intractable disease therapy is determining how long the treatment should be carried on. For RA, it would not be appropriate to stop treatment just because the target marker is stabilized. A safer indicator should be that the innate and adaptive components of the collapsed immune system are normalized to protect the body.” Koo believes that the strategy adopted by Ce-MSCNVs, where different treatment mechanisms work together, provides a unique advantage in this regard. Furthermore, she predicts that a similar approach would also be applicable to other intractable, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases for this purpose. The components within the system may also be modified. For example, other catalysts for generating ROS or other cell-derived nanovesicles could be utilized depending on the types of diseases. Overall, this study proves the potential of a hybrid nanoparticle system for the comprehensive treatment of autoimmune disease and modulation of the immune system.
Notes for editors
- References
- Media Contact
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
|
| Next | |
|---|---|
| before |
- Content Manager
- Public Relations Team : Yim Ji Yeob 042-878-8173
- Last Update 2023-11-28 14:20